The World Health Organization (WHO) reported that heart diseases were the leading cause of death in 2021, claiming 20.5 million lives. This marks a sharp increase compared to 1990, when 12.1 million people died from heart-related conditions. Of these deaths, 80% occurred in developing countries, including Rwanda.
In response to this growing health concern, King Faisal Hospital in Rwanda recently announced that, in collaboration with its partners, it successfully treated several patients with rapid heart rhythms (tachyarrhythmias) using advanced electrophysiology technology.
This effort was conducted in partnership with heart rhythm expert Prof. David Bradley from the University of Michigan. Introducing this technology in Rwanda represents a significant step forward for healthcare in the country and the region, offering hope that heart disease mortality rates will decline in the coming years.
Progress in Cardiac Care at King Faisal Hospital:
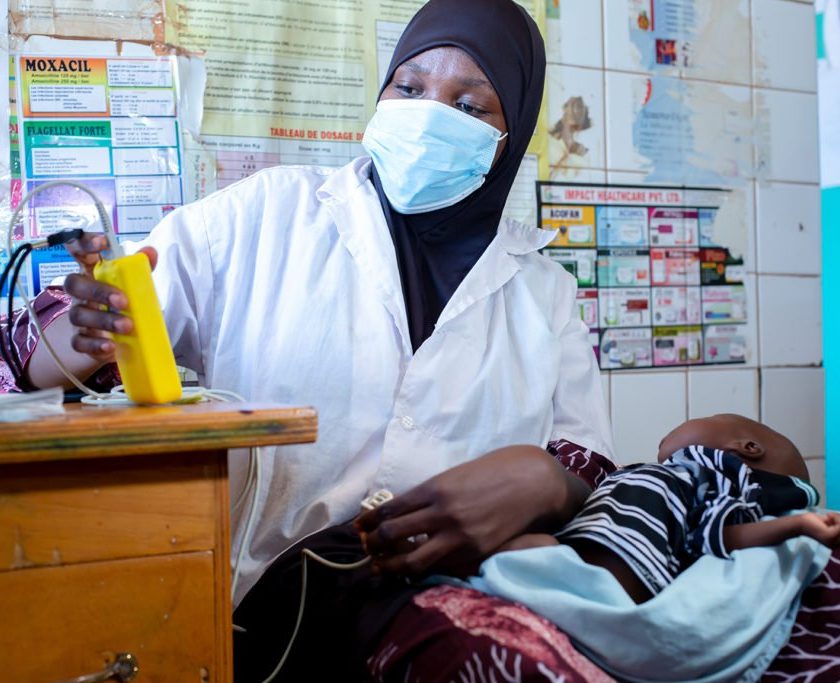
At King Faisal Hospital, multiple patients with abnormal heart rhythms were examined and treated through a procedure called “ablation,” performed on both children and adults. Hospital representatives noted, “This treatment is especially important for Rwanda, as previously, patients with these conditions would need to travel abroad to countries like India, Europe, or the United States for treatment.”
The recent procedures at King Faisal Hospital also provided a valuable training opportunity for Rwandan cardiologists, aiming to expand access to this advanced treatment across the country.
What is Electrophysiology?
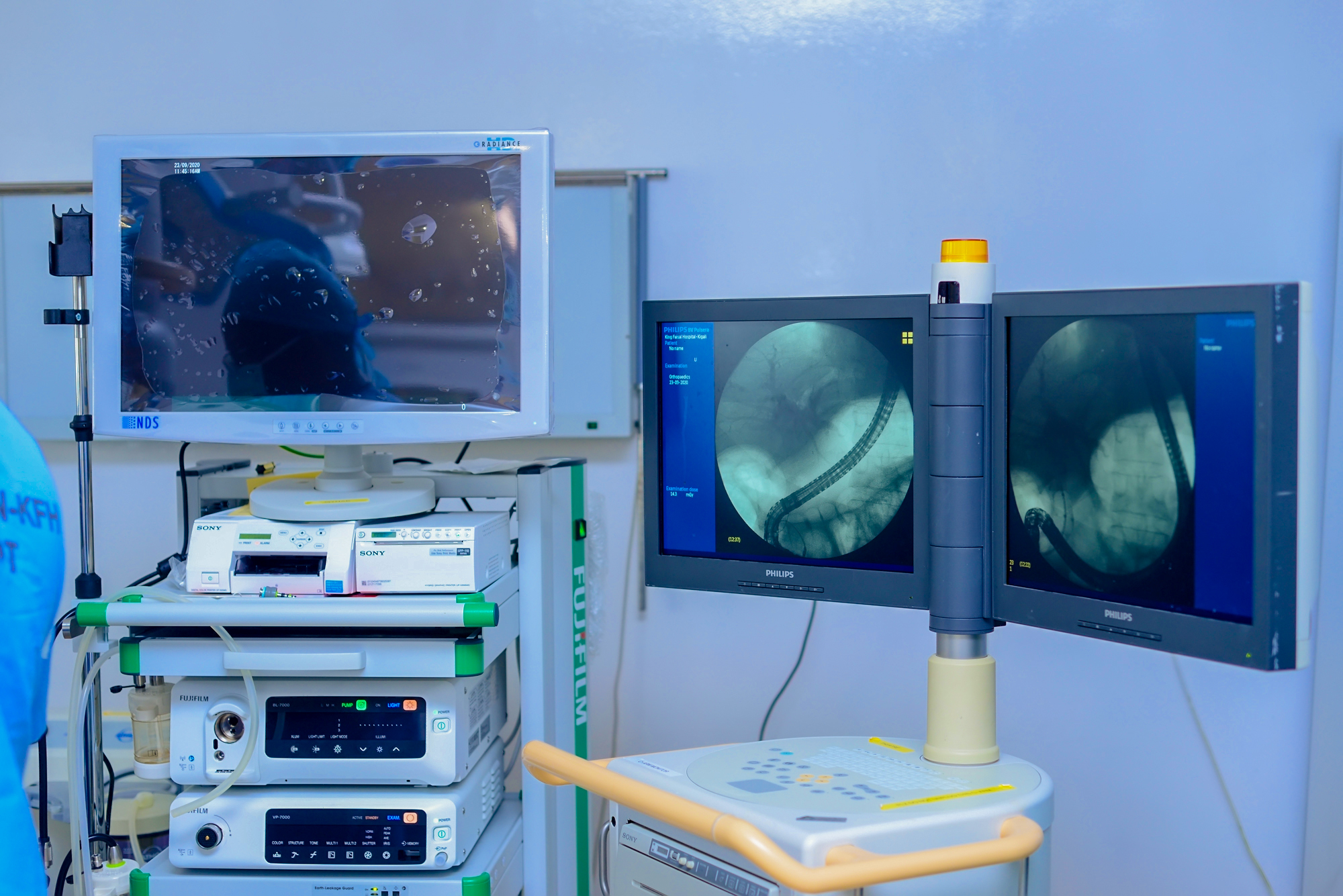
Electrophysiology (EP) is a sophisticated medical technology used to diagnose and treat heart rhythm disorders. It employs specialized tools known as “cardiac catheters,” which are extremely fine, soft tubes inserted into blood vessels leading to the heart. These catheters can be threaded through the arm, leg, or neck to reach the heart, where they help monitor blood flow, measure blood pressure, and assess heart rhythms to identify the exact origin of rhythm abnormalities.
Once the catheters are in place, they allow medical professionals to conduct precise tests, including measuring blood flow and blood pressure, examining heart rhythm irregularities, and delivering medication to specific blood vessels. During the procedure, an X-ray can be used to visualize the heart’s condition and blood flow.
Catheters are also valuable for various heart treatments, such as opening blocked arteries, sealing small holes in the heart, and correcting abnormal heart rhythms. With this technology, doctors can locate the problem area in the heart and perform a corrective procedure called “ablation” if necessary.
What is Ablation?
Ablation involves attaching a specialized device to the catheter, which delivers radiofrequency energy (heat) or cryotherapy (cold) to the affected area of the heart, effectively treating the abnormal rhythm. This technique helps to accurately target and treat heart rhythm issues without invasive surgery.
Electrophysiology and ablation provide a vital solution for diagnosing and treating heart rhythm disorders with speed and precision, making it a transformative technology for cardiac care in Rwanda.
BY KAYITESI Ange